

We link primary sources - including studies, scientific references, and statistics - within each article and also list them in the resources section at the bottom of our articles. This gives the doctor better access to remove scar tissue from the retina, repair holes, and push the retina back onto the wall of the eye.Medical News Today has strict sourcing guidelines and draws only from peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical journals and associations. The doctor removes the vitreous gel from the eye. This relieves pulling on the retina and prevents tears from getting worse. The doctor places a piece of silicone sponge, rubber, or semi-hard plastic on the outer layer of your eye and sews it in place. The eye doctor then uses a freezing probe or laser to seal the tear. The gas bubble lightly presses the detached retina to the wall of the eye. The doctor injects a gas bubble into the eyeball. Surgery is the only way to reattach the retina. They include using lasers, air bubbles, or a freezing probe to seal a tear in the retina and reattach the retina. How soon you need surgery usually depends on if the retinal detachment has or could spread far enough to affect central vision. Loss of vision can happen within a few hours or days. Without treatment, vision loss can progress from minor to severe. This is a test that uses sound waves to form an image of the retina on a computer screen. In these cases, your doctor can view the retina using ultrasound. If a retinal tear or detachment involves blood vessels in the retina, you may have bleeding in the middle of the eye. This test allows the doctor to see inside the back of the eye using a magnifying tool with a light. But they can find problems that could lead to or result from retinal detachment.Ī doctor can usually see a retinal tear or detachment while checking the retina using ophthalmoscopy. These routine vision tests don't find retinal detachment itself. The doctor will also test your near and distance vision (visual acuity) and side (peripheral) vision. You will be asked about your past eye problems and risk factors. To diagnose retinal detachment, your doctor will ask you questions about your symptoms. Or you may have new and sudden loss of side (peripheral) vision that gets worse over time. The first sign of detachment may be a shadow across part of your vision that doesn't go away. In rare cases, a retinal detachment happens without warning. But they may be a warning sign, so it's best to be checked by a doctor right away. These are actually red blood cells because all retinal tears bleed a little when they occur. Most worrisome is a shower of black dots.

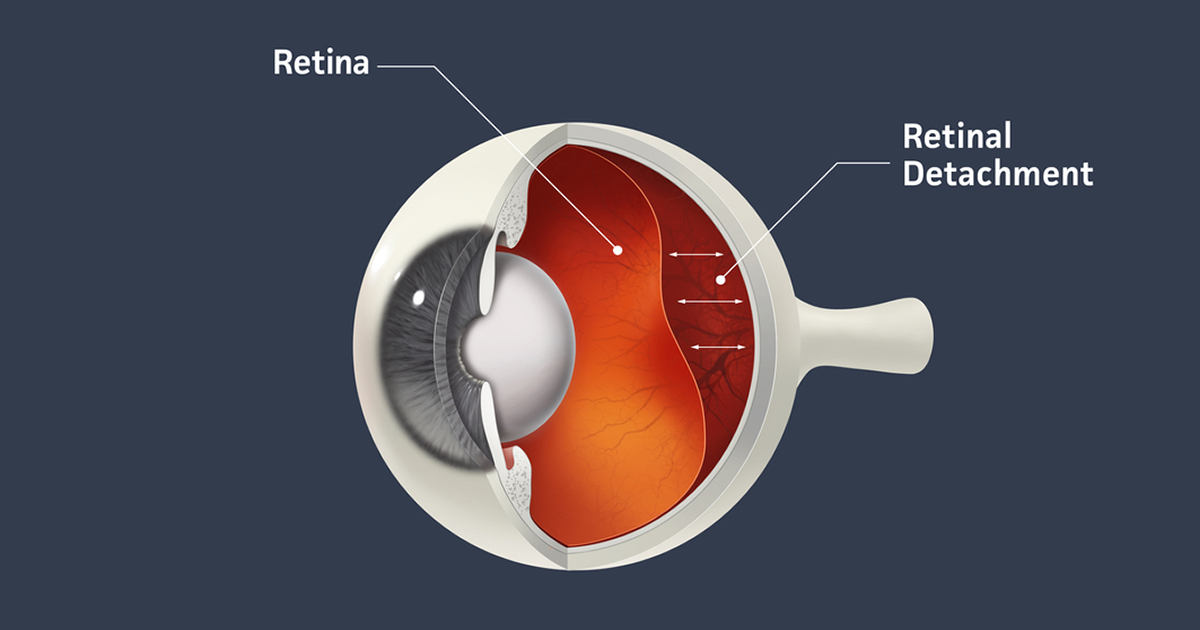
Floaters and flashes don't always mean that you will have a retinal detachment. Symptoms of a detached retina may include: The sudden appearance of 'floaters' (dark, semi-transparent, floating shapes) in the field of vision. They often appear at the edges of your visual field. Flashes are brief sparkles or lightning streaks that are easiest to see when your eyes are closed. The symptoms of retinal detachment can include the sudden appearance of floaters, flashes of light, or a shadow or curtain-like effect in the peripheral. Floaters are spots, specks, and lines that float through your field of vision. Many people see floaters and flashes of light before they have symptoms of retinal detachment. Fluid buildup may be caused by inflammation or disease in the retina, in the layer just beneath the retina (choroid), in blood vessels, or in tissues in the eye. This fluid buildup can cause the retina to come off the back of the eye. If tissue builds up between the vitreous gel and the retina, it can pull the retina away from the back of the eye. An eye or head injury or other eye disorders may also cause these tears or holes. Tears can also be caused by posterior vitreous detachment (PVD), when the vitreous gel shrinks and separates from the retina. These tears can happen when fluids collect under the retina. Retinal detachment is caused by: Tears or holes in the retina.Ī tear in the retina is the most common cause of retinal detachment. Retinal detachment requires medical care right away. But when the retina detaches, it no longer works as it should. The nerve cells in the retina normally detect light entering the eye and send signals to the brain about what the eye sees. Retinal detachment is an eye problem that happens when the retina, a thin membrane of nerve tissue that lines the back of the eye, comes off (detaches). Condition Basics What is retinal detachment?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
